Embedded carbon is a key element discussed in sustainability. It affects the entire process of a project, including a product’s end-of-life. Recarbonation is also important to the sustainability discussion - it's just talked about less.
What is embedded carbon?
Embedded carbon (also called embodied carbon) is the amount of greenhouse gas needed to produce materials. It involves the amount of energy consumed to extract, refine, process, transport, and fabricate material. Embedded carbon is expressed as a total, divided into energy from non-renewable and renewable sources (BRANZ).
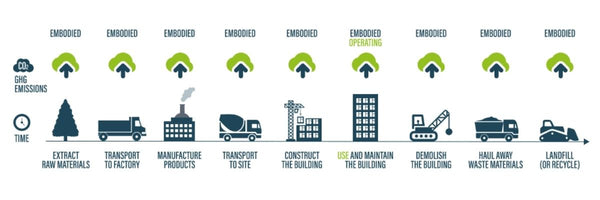
(The most common areas where embedded carbon can be found)
The phrase “embedded carbon” will be increasingly used across the construction industry. One of the main sources for this push is New Zealand's Government.
Zero Carbon Act
The Zero Carbon Act was initially passed as its own separate bill, but in May 2019, it was introduced as an amendment to the Climate Change Response Act 2002. The Act’s main focus is on drastically reducing the amount of carbon emitted in New Zealand. The target for this is zero carbon emitted by 2050 for all greenhouse gases (except biogenic methane) (MFE).
Building for Climate Change
Lowering greenhouse gas emissions across the building and construction sector is vital. It's so vital a framework called the Whole-of-Life embodied carbon reduction has been created. This framework sets compulsory reporting and measurement requirements for the whole-of-life carbon emissions, including materials used in construction, the construction process, construction waste, and the disposal of a building at its end of life (Building Performance).
Example of Embedded Carbon in Construction
Embedded carbon takes all energy used into account in the production of a material. Here is the process of creating bricks, noting the energy used (embedded carbon) at each stage.
- Energy is used to dig the raw material out of the ground
- Energy is used to shape clay, sand, and water into blocks
- Energy is used to head the shaped blocks and turn them into bricks
- Energy is used to transport bricks to the site
- Energy is used to move the bricks on site
- Energy is used if bricks are wasted if added to landfill (along with the loss of resource)
To counteract the long-term effects of embedded carbon, recarbonation takes place.
What is recarbonation in concrete?
Embedded carbon is often discussed in relation to concrete, however, there is an element that is discussed very little - recarbonation. Recarbonation is the absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere via concrete during its service life. The Global Cement and Concrete Association (GCAA) describes this as a natural process that concrete creates with the carbon dioxide in the air. Concrete can reabsorb up to 100% of the c02 emitted during the calcination of the limestone and the manufacturing process. These “process” emissions account for approximately 60% of the embodied carbon dioxide of concrete (Ready Mix News, April 2022).
How Interbloc and Stonebloc Help the Environment
Interbloc and Stonebloc both help the environment (and meet the government’s environmental policies). Although the process of creating the block systems varies, both product ranges contribute to reducing carbon emissions and provide recarbonation.
Interbloc
Interbloc is part of Envirocon’s product stewardship scheme. The scheme works alongside some of New Zealand’s leading concrete companies with the common goal of utilisting wet excess concrete. Instead of wet excess concrete going into landfill, it is diverted into Interbloc moulds. This reduces the amount of carbon emitted and eliminates a waste stream.
Once Interbloc blocks are cured, that’s when the benefits of recarbonation start to take form. As the blocks are modular, they can be used over and over again. Eventually, this leads to a 100% reabsorption rate of the embedded carbon.

(Gravity Retaining Wall made with Interbloc Concrete Blocks)
Stonebloc
Stonebloc is not part of the product stewardship scheme, but they do benefit from recarbonation. Like Interbloc, Stonebloc is a modular system that allows for non-destructive dismantling. That means, over time, the carbon emitted will be fully reabsorbed.

(Gravity Retaining Wall Made with Stonebloc Concrete Blocks)
Wanting the benefit of a concrete block system and recarbonation? Get in touch to get building with Interbloc or Stonebloc.









